The Impact of COVID-19 on Digital Learning in SA

The COVID-19 pandemic has dramatically accelerated the adoption of digital learning in South Africa, reshaping the educational landscape and highlighting existing socio-economic disparities. This article analyzes the effects of this rapid digital transformation on different groups within the country.
Accelerated Digital Adoption
The sudden closure of schools and universities due to lockdown measures forced educational institutions to swiftly implement digital learning solutions. This rapid shift has been a catalyst for digital transformation in education, pushing forward what might have otherwise taken years to achieve. However, this accelerated adoption has also brought to light significant challenges in terms of business continuity management within the education sector.
The Digital Divide
While digital learning has provided continuity for many, it has also exacerbated the existing digital divide in South Africa. Students from higher socio-economic backgrounds, typically in urban areas, have benefited from better access to devices, stable internet connections, and supportive learning environments. In contrast, those from lower-income families, often in rural areas, have faced significant barriers to accessing online education.
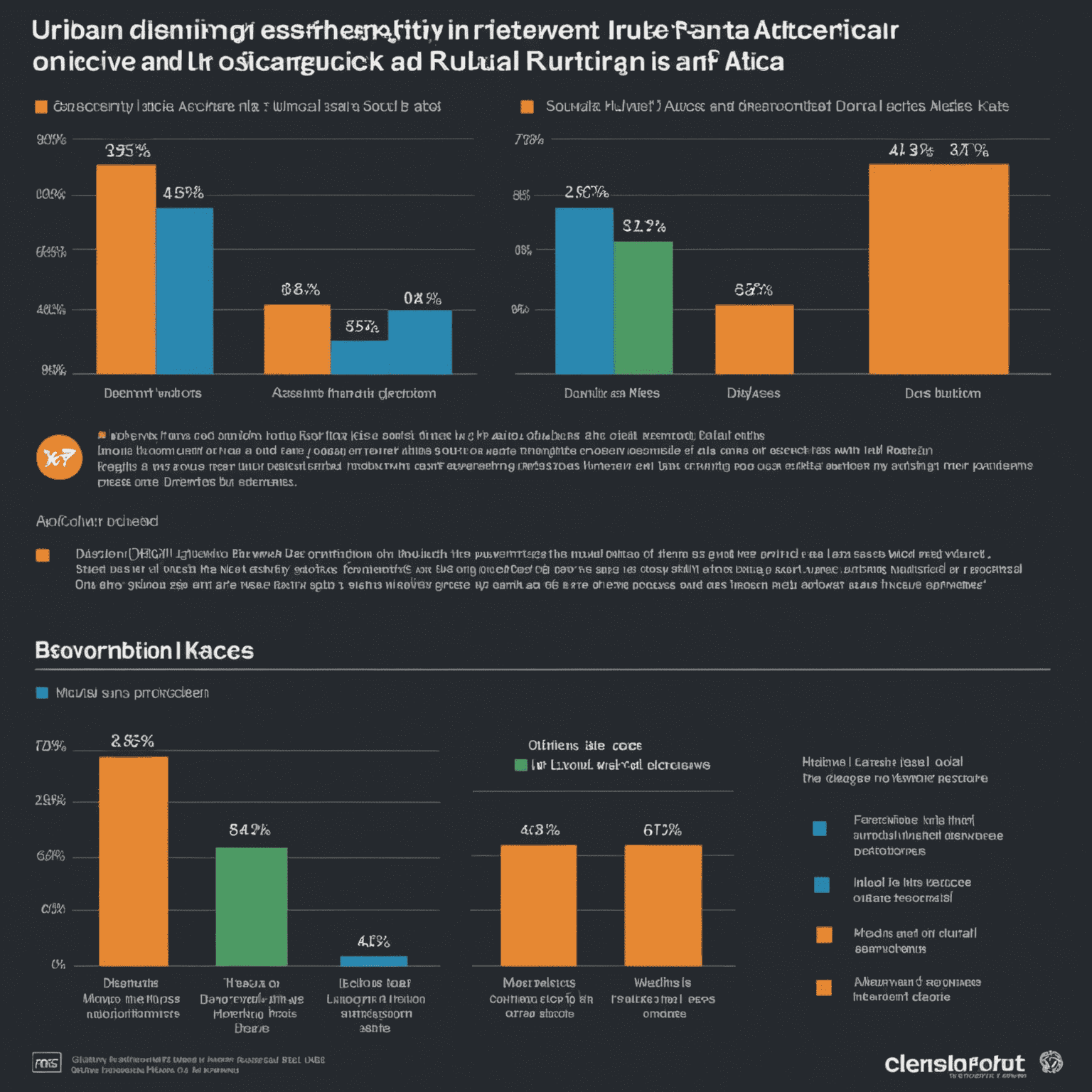
Impact on Different Socio-Economic Groups
The shift to digital learning has had varying effects across different socio-economic groups:
- Urban, middle to high-income families: Generally adapted well, with access to necessary technology and support systems.
- Township and peri-urban areas: Faced challenges with consistent internet access and device sharing among family members.
- Rural, low-income families: Experienced the most significant difficulties, often lacking basic infrastructure for digital learning.
Performance Management Challenges
The rapid transition to digital learning has also presented new challenges in terms of performance management within educational institutions. Schools and universities have had to quickly adapt their assessment methods and monitoring systems to ensure effective learning outcomes in a digital environment. This has required innovative approaches to measure student engagement, progress, and achievement.
Government and Private Sector Responses
In response to these challenges, both the government and private sector have initiated various programs:
- Distribution of devices and data packages to underprivileged students
- Development of offline learning resources for areas with poor connectivity
- Training programs for teachers on digital pedagogy
- Public-private partnerships to improve digital infrastructure in rural areas
Long-term Implications
The pandemic-induced shift to digital learning is likely to have lasting effects on South Africa's education system. While it has highlighted and, in some cases, widened existing inequalities, it has also opened up new possibilities for flexible and accessible education. The challenge moving forward will be to harness these digital advancements while ensuring equitable access and maintaining educational quality across all socio-economic groups.

Conclusion
The impact of COVID-19 on digital learning in South Africa has been profound and multifaceted. It has accelerated digital adoption in education while simultaneously exposing and exacerbating existing inequalities. As the country moves forward, addressing these disparities and ensuring inclusive access to quality digital education will be crucial for the future of learning in South Africa. This will require ongoing efforts in business continuity management and performance management to create a resilient and equitable educational system in the digital age.