Policy and Funding: Shaping SA's Digital Education Future

In the rapidly evolving landscape of South African education, government initiatives and private sector involvement are playing crucial roles in promoting equitable digital education across the nation. This article examines the intricate interplay between policy, funding, and implementation strategies aimed at bridging the digital divide in South Africa's educational system.
Government Initiatives
The South African government has recognized the importance of digital education in fostering economic growth and social equality. Recent policy frameworks have been developed to address the challenges of implementing digital learning solutions across diverse socio-economic backgrounds. These initiatives focus on:
- Infrastructure development in rural and underprivileged areas
- Teacher training programs for digital literacy
- Curriculum updates to incorporate technology-driven learning
- Performance management systems to track the progress of digital education implementation
Private Sector Involvement
The private sector has emerged as a vital partner in the government's efforts to digitize education. Companies are contributing through:
- Provision of hardware and software solutions
- Funding for pilot projects in underserved communities
- Collaboration on curriculum development to align with industry needs
- Support for business continuity management in educational institutions during transitions to digital platforms
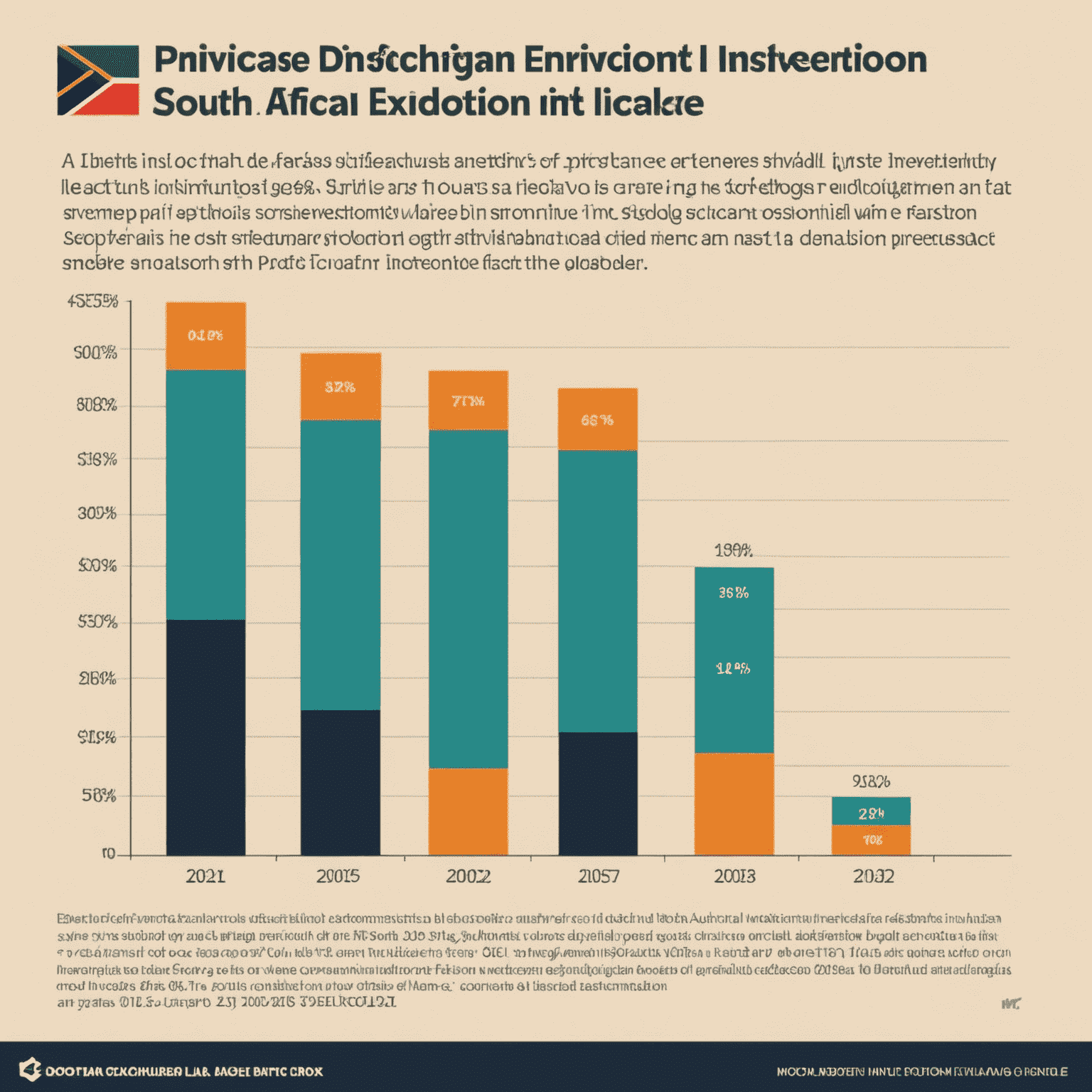
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite progress, significant challenges remain in achieving equitable digital education across South Africa:
- Uneven access to electricity and internet connectivity
- Socio-economic disparities affecting device ownership
- Resistance to change among some educators and administrators
- Balancing traditional learning methods with digital innovations
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovative solutions and collaborative efforts between the public and private sectors.
The Road Ahead
As South Africa continues to navigate its digital education journey, the following factors will be critical:
- Sustainable funding models that ensure long-term viability of digital education initiatives
- Adaptive policies that can respond to rapidly changing technological landscapes
- Robust performance management frameworks to measure the impact of digital education on learning outcomes
- Continued emphasis on business continuity management to ensure uninterrupted learning experiences
In conclusion, the future of digital education in South Africa hinges on the successful collaboration between government policy makers and private sector innovators. By addressing challenges head-on and leveraging opportunities, South Africa can create a more equitable and technologically advanced educational system that prepares its youth for the demands of the 21st-century global economy.